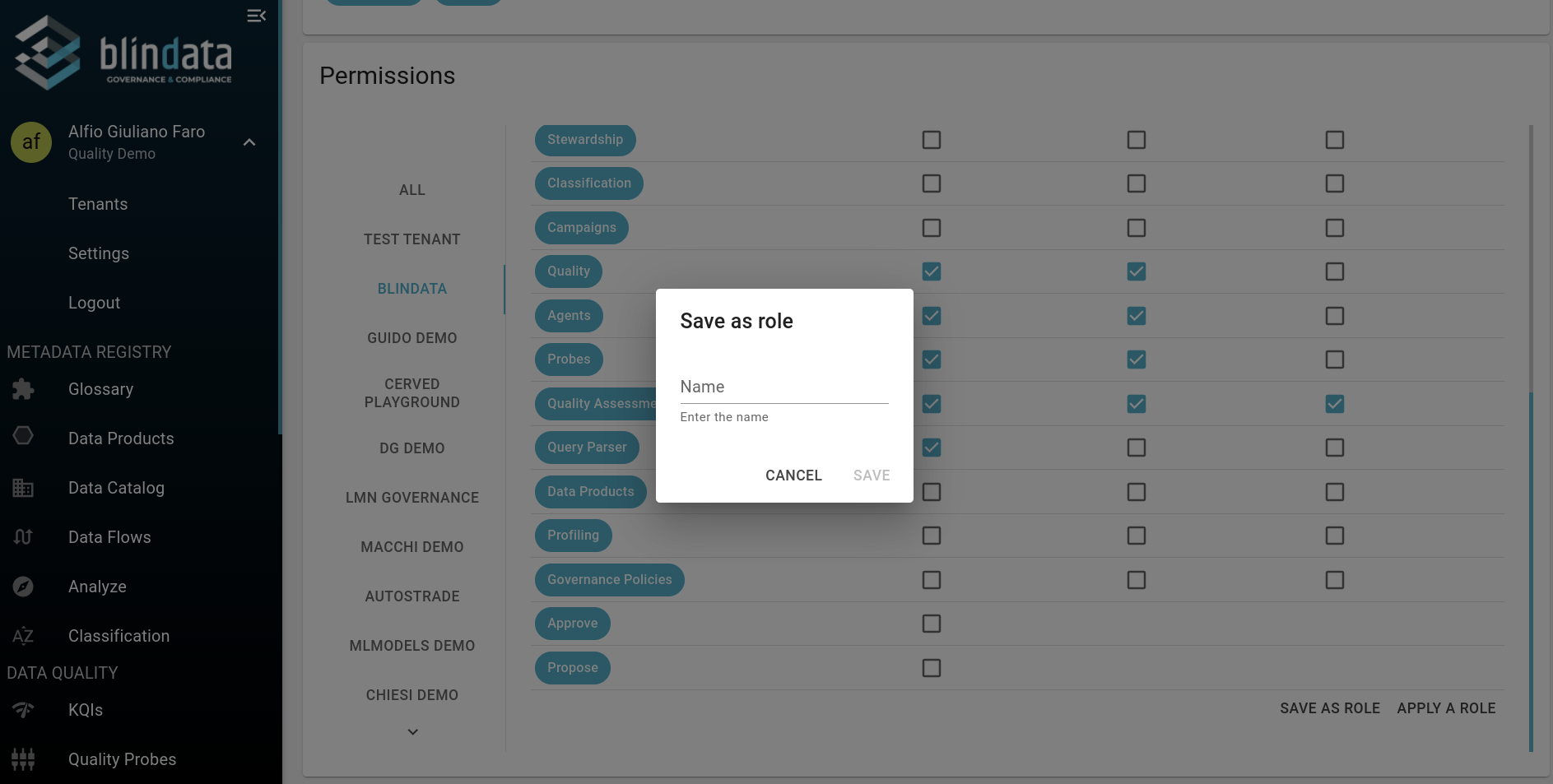
How to Give Permissions to a User
Permissions in Blindata
A permission represents a category of operations permitted for a user . Permissions enable users to perform specific actions, such as accessing or edit data. They can be set at the tenant level or instance level through the Application Scope.
To operate in a Blindata’s tenant, users must have one or more permissions associated with their user account. These permissions enable the user to access, modify, and manage information in a specific type of resources within the tenant. Generally, permissions come in three types: Viewer, Editor, and Admin.
Each user can view the active permissions on the tenant they are working on through the panel in the “Profile” section.
It is possible to modify user permissions at different levels: Tenant level and Instance level.
| Privilege | Description |
|---|---|
| Tenant Level | To modify permissions within a specific tenant, select the tenant from the left column and then interact with the matrix with the corresponding checkboxes. |
| Instance Level | To modify the permissions that apply to all tenants (i.e. the Application Scope), it is necessary to use the user modification modal and select the Application Scope. |
How to Add or Remove Permission to a User
Use the permissions matrix to add or remove permission to a user in all or a specific tenant
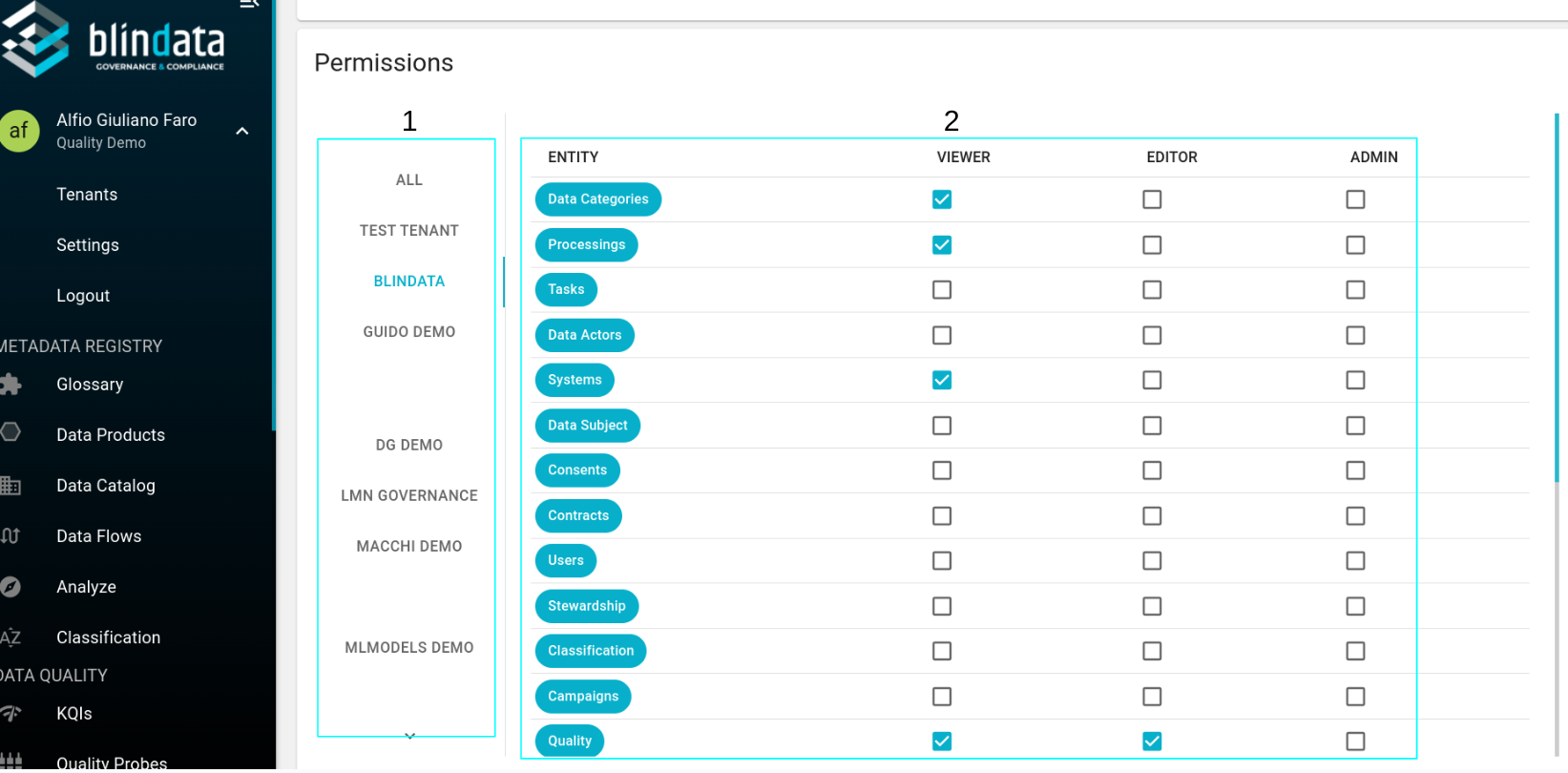
The permission matrix is subdivide in 2 sections:
-
1: List of tenants associated to the user: select a list voice to interact with user’s permission on that specific tenant.
“All” refers to the user’s general permissions that apply to any tenant.
-
2: Checkbox section: The y-axis shows the various types of resources present in Blindata, while the x-axis shows the checkboxes to add or remove the respective permission. The matrix consists of 3 columns: the first for viewer permissions, the second for editor permissions, and the third for admin permissions.
Note
Presets and Roles: It is also possible to create and save permission presets to be reused later. For more information on a Role-based management of users and permissions, please refer to the Stewardship module.